labrum tear hip test|fadir test positive means what : manufacturer The acetabulofemoral (hip) joint is the largest and most stable joint in the human body. The acetabular labrum is a soft-tissue structure . See more All components are supplied non-sterile, but may be autoclaved. *For use in laboratory research animals only. Not for use in humans .
{plog:ftitle_list}
autoclaving FeNa-EDTA and KH2PO 4 together, but separately, from other components of the medium. By eliminating precipitation and minimizing the breakdown of monosaccharides .
treatment for labral tear in hip
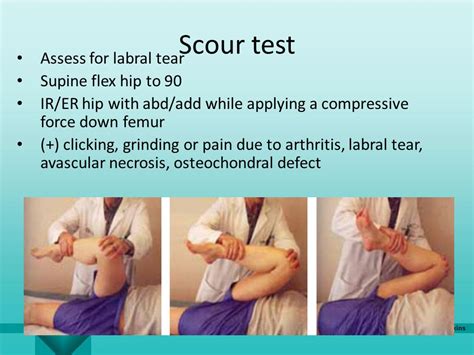
The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. See moreThe acetabulofemoral (hip) joint is the largest and most stable joint in the human body. The acetabular labrum is a soft-tissue structure . See more
light vertical multistage centrifugal pump
Step 1:The patient should be lying supine with their head supported and both arms rested to their side in a comfortable position. Step 2:The . See more Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They .The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear.
Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed pain and other symptoms, and if any activities, movements or positions make them worse.
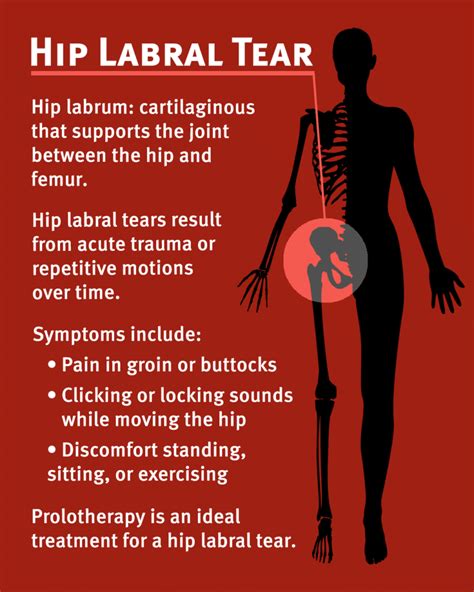
A hip labral tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. Besides cushioning the hip joint, the labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of the thighbone securely within the hip socket. A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.Diagnosing labral tears in the hip involves: Evaluating the hip joint to check for labral problems; Conducting specific hip labral tear tests to determine if the labrum may be torn or degenerated; Identifying or ruling out other hip conditions contributing to the patient’s symptoms
Plain radiographs and computed tomography may show hip dysplasia, arthritis, and acetabular cysts in patients with acetabular labrum tears, they are useful for excluding other types of hip pathology. MRI helps in diagnosing acetabular labral tears.What You Need to Know. A labral tear is an injury to the tissue that holds the ball and socket parts of the hip together. Torn hip labrum may cause pain, reduced range of motion in the hip and a sensation of the hip locking up.When the labrum tears, it can cause pain and hip instability. A torn labrum also increases the risk of developing osteoarthritis of the hip, a painful and potentially debilitating condition. Fortunately, treatments are available for hip labral tears, including nonsurgical and surgical options. What is a labral tear of the hip? A labral tear of the hip is an injury of the hip labrum. This tough, crescent-shaped cartilage structure lines the rim of the hip socket (called the acetabulum), which is located in the pelvic bone.
The McCarthy Test is a clinical test used in the diagnosis of a hip labral tear. The shearing force-producing painful popping, clicking, or catching while performing the test indicates a possible hip labrum tear. Imaging scans. A hip labral tear rarely occurs by itself. In most cases, other structures within the hip joint also have injuries. X-rays are excellent at visualizing bone. They can check for arthritis and for structural problems.A healthcare provider will diagnose a hip labral tear with a physical exam and some tests. They’ll examine your hip and ask you about your symptoms. Tell your provider when you first noticed pain and other symptoms, and if any activities, movements or positions make them worse. A hip labral tear involves the ring of cartilage (labrum) that follows the outside rim of the hip joint socket. Besides cushioning the hip joint, the labrum acts like a rubber seal or gasket to help hold the ball at the top of the thighbone securely within the hip socket.
A hip labral tear is a traumatic tear of the acetabular labrum, mostly common seen in acetabular dysplasia, that may lead to symptoms of internal snapping hip as well hip locking with hip range of motion. Diagnosis generally requires an MR arthrogram of the hip joint in question.Diagnosing labral tears in the hip involves: Evaluating the hip joint to check for labral problems; Conducting specific hip labral tear tests to determine if the labrum may be torn or degenerated; Identifying or ruling out other hip conditions contributing to the patient’s symptomsPlain radiographs and computed tomography may show hip dysplasia, arthritis, and acetabular cysts in patients with acetabular labrum tears, they are useful for excluding other types of hip pathology. MRI helps in diagnosing acetabular labral tears.
What You Need to Know. A labral tear is an injury to the tissue that holds the ball and socket parts of the hip together. Torn hip labrum may cause pain, reduced range of motion in the hip and a sensation of the hip locking up.When the labrum tears, it can cause pain and hip instability. A torn labrum also increases the risk of developing osteoarthritis of the hip, a painful and potentially debilitating condition. Fortunately, treatments are available for hip labral tears, including nonsurgical and surgical options.
labral tear physical exam tests
labral special tests hip
oil water separator centrifuge
how can one heal a hip labral tear
When autoclaving Nalgene™ bottles and carboys, completely disengage the .
labrum tear hip test|fadir test positive means what